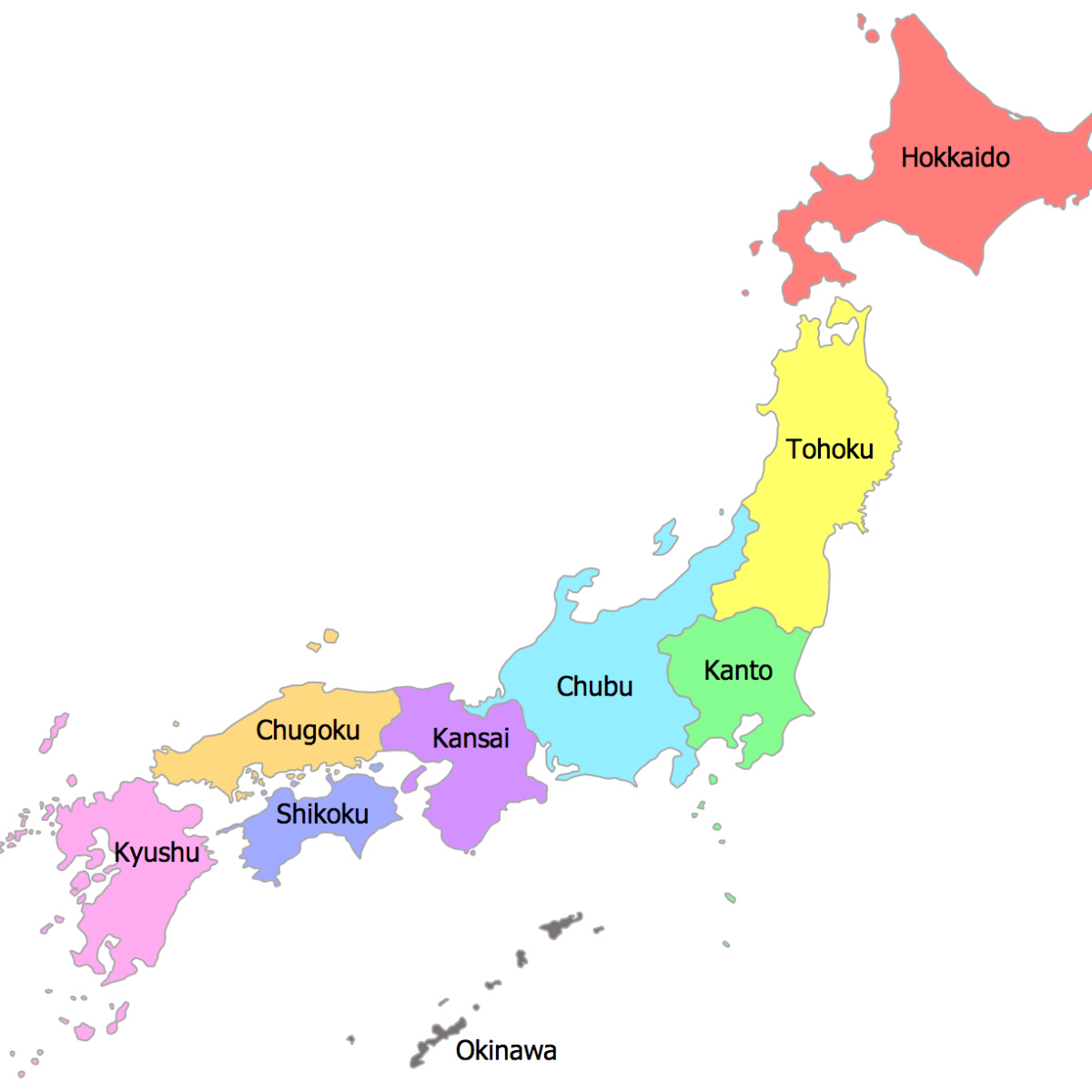
Japan is an archipelago (means a chain of islands) in East Asia, consisting of four main islands (Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku) and thousands of smaller islands.
Its geography is diverse, featuring mountains, forests, coastal plains, and volcanic activity. Let’s explore Japan’s regions, their geography, and some important places or facts about each:
1. Hokkaido (北海道)
Geography: Japan’s northernmost island, known for its cold winters, vast plains, and volcanic mountains.
Important Places:
Sapporo: The capital, famous for the Sapporo Snow Festival and its beer.
Furano: Known for its lavender fields and scenic landscapes.
Shiretoko National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site with pristine wilderness and wildlife.
Facts:
Hokkaido is Japan’s largest prefecture by area but has a relatively low population density.
It’s a hub for winter sports, with world-class ski resorts like Niseko.
2. Tohoku (東北)
Geography: Located in northern Honshu, this region is mountainous and known for its rugged coastline, hot springs, and rural landscapes.
Important Places:
Sendai: The largest city, known as the "City of Trees" and home to the Tanabata Festival.
Matsushima: One of Japan’s "Three Most Scenic Views," featuring a bay dotted with pine-covered islands.
Hiraizumi: A UNESCO World Heritage Site with historic temples and gardens.
Facts:
Tohoku is famous for its rice production, particularly the high-quality Akitakomachi and Hitomebore varieties.
The region was heavily affected by the 2011 earthquake and tsunami but has since made significant recovery efforts.
3. Kanto (関東)
Geography: Located in eastern Honshu, this region includes the Tokyo metropolitan area and surrounding prefectures.
Important Places:
Tokyo: Japan’s capital, a global city known for its skyscrapers, historic temples, and vibrant culture.
Nikko: A UNESCO World Heritage Site with stunning shrines and natural beauty.
Yokohama: Japan’s second-largest city, known for its Chinatown and waterfront.
Facts:
Kanto is Japan’s most populous and economically powerful region.
The area is prone to earthquakes, including the Great Kanto Earthquake of 1923.
4. Chubu (中部)
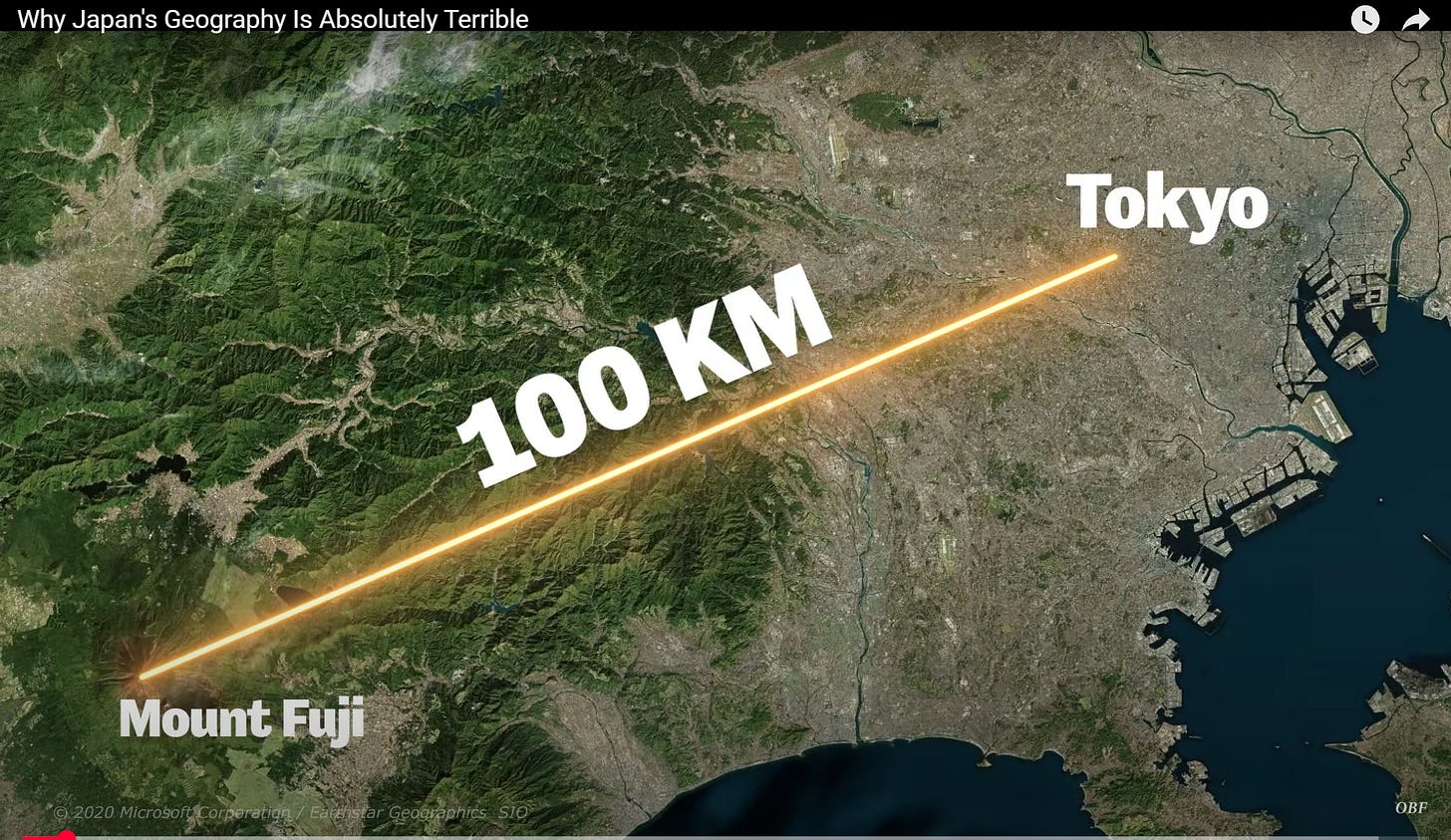
Geography: Central Honshu, featuring the Japanese Alps, Mount Fuji, and both Pacific and Sea of Japan coastlines.
Important Places:
Nagoya: The region’s largest city, known for its automotive industry and Nagoya Castle.
Takayama: A beautifully preserved historic town with traditional architecture.
Mount Fuji: Japan’s highest peak and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Monkey Hot springs.
Facts:
The Japanese Alps offer world-class hiking and skiing opportunities.
Chubu is home to the Shinkansen (bullet train) line connecting Tokyo and Osaka.
5. Kansai (関西)
Geography: Located in western Honshu, this region is known for its historical and cultural significance.
Important Places:
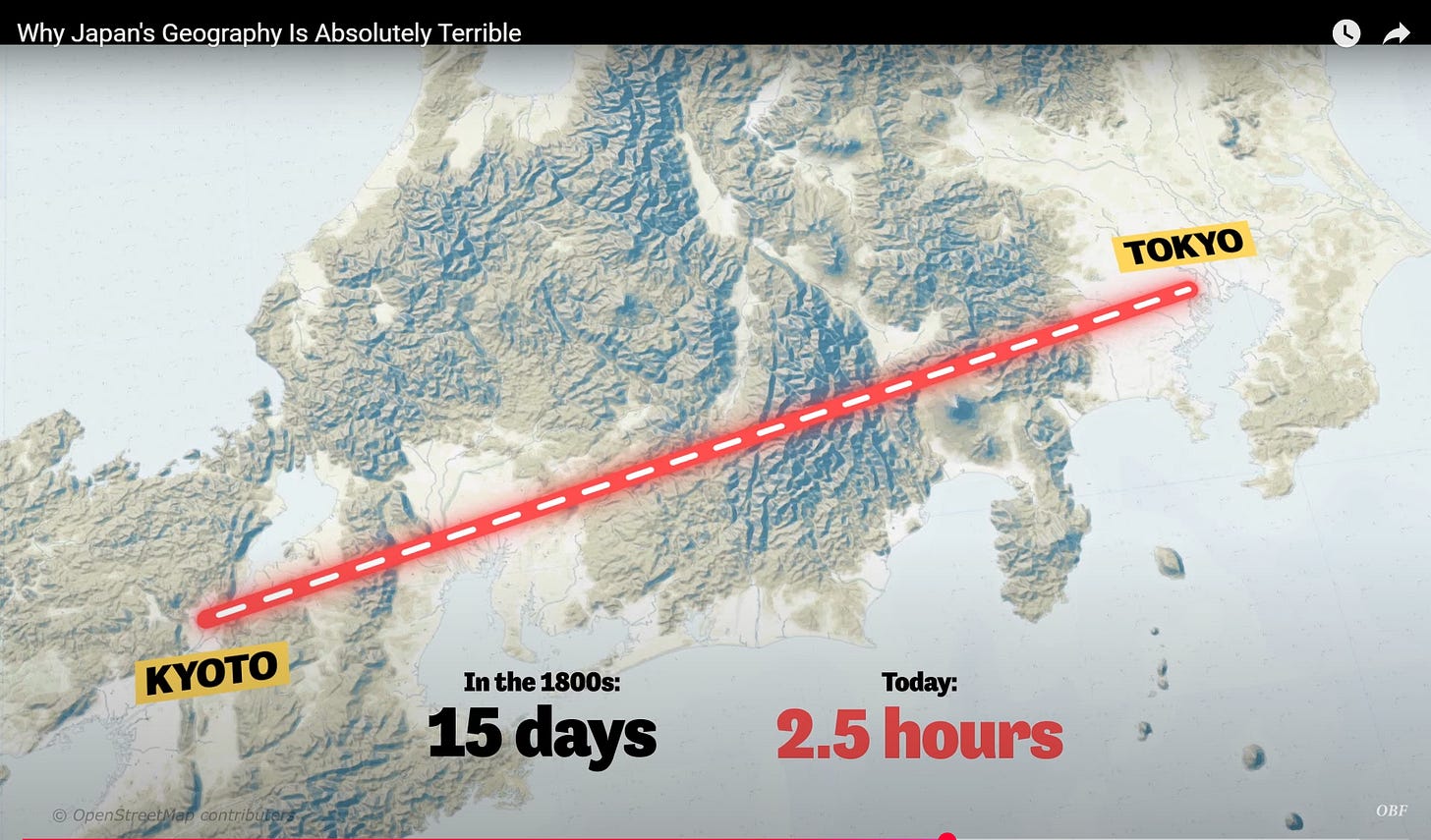
Kyoto: Japan’s ancient capital, famous for its temples, shrines, and traditional tea houses.
Osaka: A bustling city known for its food culture (e.g., takoyaki and okonomiyaki) and Osaka Castle.
Nara: Home to Todai-ji Temple and the famous Nara deer.
Facts:
Kansai is considered the cultural heart of Japan, with a distinct dialect and traditions. Homeland of Ninjas.
Famous temples.
6. Chugoku (中国)
Geography: Western Honshu, featuring coastal plains, mountains, and the Seto Inland Sea.
Important Places:
Hiroshima: Known for the Peace Memorial Park and Atomic Bomb Dome.
Miyajima: An island famous for the "floating" Torii gate of Itsukushima Shrine.
Okayama: Home to Korakuen Garden, one of Japan’s three great gardens.
Facts:
Chugoku is known for its citrus fruits, particularly mikan (mandarin oranges).
The region played a significant role in Japan’s industrialization during the Meiji era.
7. Shikoku (四国)
Geography: The smallest of Japan’s four main islands, known for its mountainous terrain and pilgrimage routes.
Important Places:
Matsuyama: Home to Matsuyama Castle and Dogo Onsen, one of Japan’s oldest hot springs.
Naoshima: An island famous for its contemporary art museums and installations.
Iya Valley: A remote area with stunning gorges and vine bridges.
Facts:
Shikoku is famous for the 88 Temple Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer route visited by Buddhist pilgrims.
The island is connected to Honshu by the Seto Ohashi Bridge, one of the longest bridge systems in the world.
National Dog. Also look for the movie and story of Hachiko.
8. Kyushu (九州)
Geography: Japan’s southernmost main island, known for its active volcanoes, hot springs, and subtropical climate.
Important Places:
Fukuoka: The largest city, known for its vibrant food scene and Hakata ramen.
Nagasaki: A historic port city with a rich cultural heritage and Peace Park.
Beppu: A hot spring resort town with unique geothermal attractions.
Facts:
Kyushu is the gateway to Japan’s southern islands, including Okinawa.
The region is known for its tonkotsu ramen and shochu (a distilled spirit).
Also search for underwater tunnels
9. Okinawa (沖縄)
Geography: A chain of subtropical islands in the far south, known for their coral reefs, beaches, and unique culture.
Important Places:
Naha: The capital, home to Shuri Castle and Kokusai Street.
Ishigaki: Known for its pristine beaches and diving spots.
Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium: One of the largest aquariums in the world.
Facts:
Okinawa has a distinct culture influenced by its history as the Ryukyu Kingdom.
The region is known for its longevity, with one of the highest life expectancies in the world.
Okinawa is home of Karate.
Key Geographic Features of Japan
Mountains: Over 70% of Japan is mountainous, with the Japanese Alps and Mount Fuji being prominent.
Volcanoes: Japan has over 100 active volcanoes, including Mount Aso and Mount Sakurajima.
Coastlines: Japan has a long coastline, with the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west.
Earthquakes: Located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Japan is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis.